10 【Express基本使用】
10 【Express基本使用】
基于 Node.js 平台,快速、开放、极简的 web 开发框架。
1.Express的安装方式
Express的安装可直接使用npm包管理器上的项目,在安装npm之前可先安装淘宝镜像:
npm install -g cnpm --registry=https://registry.npmmirror.com/
这样我们使用cnpm的来代替npm,这使得下载速度提高很多;其次你需要在你项目目录下运行以下指令来初始化npm,期间所有提示按enter键即可,这会生成package.json,它是用于描述项目文件的。
cnpm init
再输入
cnpm install
这下项目目录中又会多出一个叫node_modules文件夹,里面是node.js为我们提供的模块,当然现在没有。接下来便是真正的安装express了,执行:
cnpm install express --save
这时,我们看到node_modules文件夹多了许多不同版本的应用文件夹,接下来执行
express --version
查看express是否安装成功,如果显示版本号,则安装正确。

2.运行原理
底层:http模块
Express框架建立在node.js内置的http模块上。http模块生成服务器的原始代码如下
var http = require("http");
var app = http.createServer(function(request, response) {
response.writeHead(200, {"Content-Type": "text/plain"});
response.end("Hello world!");
});
app.listen(3000, "localhost");
Express框架的核心是对http模块的再包装。上面的代码用Express改写如下
var express = require('express');
var app = express();
app.get('/', function (req, res) {
res.send('Hello world!');
});
app.listen(3000);
Express框架等于在http模块之上,加了一个中间层
什么是中间件
- 简单说,中间件(middleware)就是处理HTTP请求的函数。它最大的特点就是,一个中间件处理完,再传递给下一个中间件。App实例在运行过程中,会调用一系列的中间件
- 每个中间件可以从App实例,接收三个参数,依次为request对象(代表HTTP请求)、response对象(代表HTTP回应),next回调函数(代表下一个中间件)。每个中间件都可以对HTTP请求(request对象)进行加工,并且决定是否调用next方法,将request对象再传给下一个中间件。
- 一个不进行任何操作、只传递
request对象的中间件,就是下面这样
function uselessMiddleware(req, res, next) {
next();
}
- 上面代码的next就是下一个中间件。如果它带有参数,则代表抛出一个错误,参数为错误文本
- 抛出错误以后,后面的中间件将不再执行,直到发现一个错误处理函数为止
function uselessMiddleware(req, res, next) {
next('出错了!');
}
3.Express 方法
Express路由简介
路由表示应用程序端点 (URI) 的定义以及响应客户端请求的方式。它包含一个请求方时(methods)、路径(path)和路由匹配时的函数(callback);
app.methods(path, callback);
Express路由方法
Express方法源于 HTTP 方法之一,附加到 express 类的实例。它可请求的方法包括:
get、post、put、head、delete、options、trace、copy、lock、mkcol、move、purge、propfind、proppatch、unlock、report、mkactivity、checkout、merge、m-search、notify、subscribe、unsubscribe、patch、search 和 connect。
路由是指如何定义应用的端点(URIs)以及如何响应客户端的请求。
路由是由一个 URI、HTTP 请求(GET、POST等)和若干个句柄组成,它的结构如下: app.METHOD(path, [callback...], callback), app 是 express 对象的一个实例, METHOD 是一个 HTTP 请求方法, path 是服务器上的路径, callback 是当路由匹配时要执行的函数。
下面是一个基本的路由示例:
var express = require('express');
var app = express();
// respond with "hello world" when a GET request is made to the homepage
app.get('/', function(req, res) {
//写完一个send,后面所有跟路由有关的都不会执行
//会自动响应对应的数据类型
// res.send([1, 2, 3]);
// res.send({ ok: 1 });
// res.json({ ok: 1 });
// 使用混合使用函数数组处理时如果前面有res.send();那么后面和路由处理相关代码都不生效
res.send('hello world');
res.send(`
<html>
<h1>hello world</h2>
</html>
`);
});
路由路径和请求方法一起定义了请求的端点,它可以是字符串、字符串模式或者正则表达式。
all方法和HTTP动词方法
针对不同的请求,Express提供了use方法的一些别名。比如,上面代码也可以用别名的形式来写
var express = require("express");
var http = require("http");
var app = express();
app.all("*", function(request, response, next) {
response.writeHead(200, { "Content-Type": "text/plain" });
next();
});
app.get("/", function(request, response) {
response.end("Welcome to the homepage!");
});
app.get("/about", function(request, response) {
response.end("Welcome to the about page!");
});
app.get("*", function(request, response) {
response.end("404!");
});
http.createServer(app).listen(1337);
- 上面代码的all方法表示,所有请求都必须通过该中间件,参数中的“*”表示对所有路径有效。get方法则是只有GET动词的HTTP请求通过该中间件,它的第一个参数是请求的路径。由于get方法的回调函数没有调用next方法,所以只要有一个中间件被调用了,后面的中间件就不会再被调用了
- 除了get方法以外,Express还提供post、put、delete方法,即HTTP动词都是Express的方法
- 除了get方法以外,Express还提供post、put、delete方法,即HTTP动词都是Express的方法
- 这些方法的第一个参数,都是请求的路径。除了绝对匹配以外,Express允许模式匹配
app.get("/hello/:who", function(req, res) {
res.end("Hello, " + req.params.who + ".");
});
4.路径匹配
4.1 字符串路径
// 匹配根路径的请求
app.get('/', function (req, res) {
res.send('root');
});
// 匹配 /about 路径的请求
app.get('/about', function (req, res) {
res.send('about');
});
// 匹配 /random.text 路径的请求
app.get('/random.text', function (req, res) {
res.send('random.text');
});
4.2 字符串模式路径
使用字符串模式的路由路径示例:
// 匹配 acd 和 abcd
app.get('/ab?cd', function(req, res) {
res.send('ab?cd');
});
// 匹配 abcd、abbcd、abbbcd等
app.get('/ab+cd', function(req, res) {
res.send('ab+cd');
});
// 匹配 abcd、abxcd、abRABDOMcd、ab123cd等
app.get('/ab*cd', function(req, res) {
res.send('ab*cd');
});
// 匹配 /abe 和 /abcde
app.get('/ab(cd)?e', function(req, res) {
res.send('ab(cd)?e');
});
4.3 正则表达式路径
使用正则表达式的路由路径示例:
// 匹配任何路径中含有 a 的路径:
app.get(/a/, function(req, res) {
res.send('/a/');
});
// 匹配 butterfly、dragonfly,不匹配 butterflyman、dragonfly man等
app.get(/.*fly$/, function(req, res) {
res.send('/.*fly$/');
});
可以为请求处理提供多个回调函数,其行为类似 中间件。唯一的区别是这些回调函数有可能调用 next('route') 方法而略过其他路由回调函数。可以利用该机制为路由定义前提条件,如果在现有路径上继续执行没有意义,则可将控制权交给剩下的路径。
app.get('/example/a', function (req, res) {
res.send('Hello from A!');
});
使用多个回调函数处理路由(记得指定 next 对象):
app.get('/example/b', function (req, res, next) {
console.log('response will be sent by the next function ...');
next();
}, function (req, res) {
res.send('Hello from B!');
});
使用回调函数数组处理路由:
var cb0 = function (req, res, next) {
console.log('CB0')
next()
}
var cb1 = function (req, res, next) {
console.log('CB1')
next()
}
var cb2 = function (req, res) {
res.send('Hello from C!')
}
app.get('/example/c', [cb0, cb1, cb2])
5.response对象
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| res.download() | 提示要下载的文件。 |
| res.end() | 结束响应过程。 |
| res.json() | 发送JSON响应。 |
| res.jsonp() | 发送带有JSONP支持的JSON响应。 |
| res.redirect() | 重定向请求。 |
| res.render() | 渲染视图模板。 |
| res.send() | 发送各种类型的响应。 |
| res.sendFile() | 将文件作为八位字节流发送。 |
| res.sendStatus() | 设置响应状态代码,并将其字符串表示形式发送为响应正文。 |
例:
(1)response.redirect方法
response.redirect方法允许网址的重定向
response.redirect("/hello/anime");
response.redirect("http://www.example.com");
response.redirect(301, "http://www.example.com");
(2)response.sendFile方法
response.sendFile方法用于发送文件
response.sendFile("/path/to/anime.mp4");
(3)response.render方法
response.render方法用于渲染网页模板。
// 使用render方法,将message变量传入index模板,渲染成HTML网页
app.get("/", function(request, response) {
response.render("index", { message: "Hello World" });
});
6.路线处理程序
您可以提供行为类似于中间件的多个回调函数来处理请求。唯一的例外是这些回调可能会调用next('route')以绕过其余的路由回调。您可以使用此机制在路由上施加先决条件,然后在没有理由继续使用当前路由的情况下将控制权传递给后续路由。
多个回调函数可以处理一条路由(确保指定了next对象)。例如:
app.get('/example/b', function (req, res, next) {
console.log('the response will be sent by the next function ...')
next()
}, function (req, res) {
res.send('Hello from B!')
})
混合使用函数和函数数组处理路由:
const fun1 = (req, res, next) => {
// 验证用户token过期, cookie过期
console.log('token验证');
let isValid = true;
if (isValid) {
next();
} else {
//将第一个中间件的数据传输到第二个中间件
res.name = "dselegent";
res.send('error');
}
};
const fun2 = (req, res) => {
console.log(res.name)
res.send('home');
};
app.get('/home', [fun1, fun2]);
app.get('/list', fun1, (req, res) => {
res.send('list');
});
7.中间件
Express 是一个自身功能极简,完全是由路由和中间件构成一个的 web 开发框架:从本质上来说,一个 Express 应用就是在调用各种中间件。
中间件(Middleware) 是一个函数,它可以访问请求对象(request object (req)), 响应对象(response object (res)), 和 web 应用中处于请求-响应循环流程中的中间件,一般被命名为 next 的变量。
中间件的功能包括:
- 执行任何代码。
- 修改请求和响应对象。
- 终结请求-响应循环。
- 调用堆栈中的下一个中间件。
如果当前中间件没有终结请求-响应循环,则必须调用 next() 方法将控制权交给下一个中间件,否则请求就会挂起。
Express 应用可使用如下几种中间件:
- 应用级中间件
- 路由级中间件
- 错误处理中间件
- 内置中间件
- 第三方中间件
使用可选则挂载路径,可在应用级别或路由级别装载中间件。另外,你还可以同时装在一系列中间件函数,从而在一个挂载点上创建一个子中间件栈。
7.1 应用级中间件
应用级中间件绑定到 app 对象 使用 app.use() 和 app.METHOD(), 其中, METHOD 是需要处理的 HTTP 请求的方法,例如 GET, PUT, POST 等等,全部小写。例如:
var app = express()
const indexRouter = require('./route/indexRouter');
const LoginRouter = require('./route/LoginRouter');
//应用级别(后面的路由都会执行此中间件)
app.use((req, res, next) => {
// 验证用户token过期, cookie过期
console.log('token验证');
let isValid = true;
if (isValid) {
next();
} else {
res.send('error');
}
});
//应用级别(这里不写路径默认/)
//这些use方法是每次访问都是从上往下执行
//如果是/login/a,会先找到/login开头的这个应用级中间件
//然后再进入这个中间件找/a
app.use(indexRouter);
app.use('/login', LoginRouter);
7.2 路由级中间件
7.2.1 app.route()
您可以使用来为路由路径创建可链接的路由处理程序app.route()。由于路径是在单个位置指定的,因此创建模块化路由非常有帮助,减少冗余和错别字也很有帮助。有关路由的更多信息,请参见:Router()文档。
这是使用定义的链式路由处理程序的示例app.route()。
app.route('/book')
.get(function (req, res) {
res.send(' Get a random book')
})
.post(function (req, res) {
res.send('Add a book')
})
.put(function (req, res) {
res.send('Update the book')
})
7.2.2 快速路由器
路由级中间件和应用级中间件一样,只是它绑定的对象为 express.Router()。
使用express.Router该类创建模块化的,可安装的路由处理程序。一个Router实例是一个完整的中间件和路由系统; 因此,它通常被称为“迷你应用程序”。
以下示例将路由器创建为模块,在其中加载中间件功能,定义一些路由,并将路由器模块安装在主应用程序的路径上。
home.js在app目录中创建一个名为以下内容的路由器文件:
var router = express.Router()
var app = express()
var router = express.Router()
// 没有挂载路径的中间件,通过该路由的每个请求都会执行该中间件
router.use(function (req, res, next) {
console.log('Time:', Date.now())
next()
})
// 一个中间件栈,显示任何指向 /user/:id 的 HTTP 请求的信息
router.use('/user/:id', function(req, res, next) {
console.log('Request URL:', req.originalUrl)
next()
}, function (req, res, next) {
console.log('Request Type:', req.method)
next()
})
// 一个中间件栈,处理指向 /user/:id 的 GET 请求
router.get('/user/:id', function (req, res, next) {
// 如果 user id 为 0, 跳到下一个路由
if (req.params.id == 0) next('route')
// 负责将控制权交给栈中下一个中间件
else next() //
}, function (req, res, next) {
// 渲染常规页面
res.render('regular')
})
// 处理 /user/:id, 渲染一个特殊页面
router.get('/user/:id', function (req, res, next) {
console.log(req.params.id)
res.render('special')
})
module.exports= router
然后,在应用程序中加载路由器模块:
var indexRouter = require('./home')
// ...
app.use('/home', index)
该应用程序现在将能够处理对/home和的请求/home/user/123456
7.2.3 router.route方法
router实例对象的route方法,可以接受访问路径作为参数
var router = express.Router();
router.route('/api')
.post(function(req, res) {
// ...
})
.get(function(req, res) {
Bear.find(function(err, bears) {
if (err) res.send(err);
res.json(bears);
});
});
module.exports= router
7.3 错误处理中间件
错误处理中间件和其他中间件定义类似,只是要使用 4 个参数,而不是 3 个,其签名如下: (err, req, res, next)。
//上面的中间件都没有匹配就会走这里
app.use(function(err, req, res, next) {
console.error(err.stack)
//send的状态码默认是200
res.status(500).send('error')
})
7.4 内置的中间件
express.static 是 Express 唯一内置的中间件。它基于 serve-static,负责在 Express 应用中提托管静态资源。每个应用可有多个静态目录。
app.use(express.static('public'))
app.use(express.static('uploads'))
app.use(express.static('files'))
7.5 第三方中间件
安装所需功能的 node 模块,并在应用中加载,可以在应用级加载,也可以在路由级加载。
下面的例子安装并加载了一个解析 cookie 的中间件: cookie-parser
$ npm install cookie-parser
var express = require('express')
var app = express()
var cookieParser = require('cookie-parser')
// 加载用于解析 cookie 的中间件
app.use(cookieParser())
8.获取参数
8.1 req.query
req.query()可以用来获取接口请求中拼接在链接"?"后边的参数,主要用于get请求,post请求也适用。 req.query()被express原生支持,并且会自动将参数转换为对象形式返回。 请求:
http://localhost:5050/server?p=user&q=password
express接口:
let express = require('express')
let server = express()
server.get('/server',(req,resp)=>{
console.log(req.query);
resp.send('')
})
server.listen(5050,()=>{
console.log('服务器已就绪')
})
请求后得到的结果:

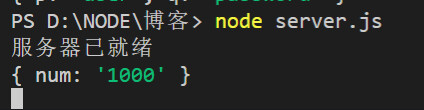
8.2 req.params
req.params()有些特殊,它适用于在url链接上传递数据参数,需要后台接口用==:变量名==的写法发起请求。
请求:
http://localhost:5050/nums/1000
express接口:
let express = require('express')
let server = express();
server.get('/nums/:num', (req, resp) => {
console.log(req.params);
resp.send('')
})
server.listen(5050, () =>{
console.log('服务器已就绪')
})
请求后得到的结果:
8.3 req.body
req.body()被原生express所支持,可以直接使用req.body()获取post请求的表单数据。
请求:
fecth('http://localhost:5050/people',{
method: 'post',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
},
body:{name: 'zhangsan', age: 15}
})
express接口:
const express = require('express');
const server = express();
//配置解析post参数的-不用下载第三方 ,内置
//解析post参数-(url-ky格式) username=kerwin&password=1234
// app.use(express.urlencoded({ extended: false }));
//解析post参数-(json字符串) {name:"",age:100}
app.use(express.json());
server.post('/people', (req, resp) => {
console.log(req.body);
resp.send('')
})
server.listen(5050, () => console.log('服务器已就绪'))

9.利用 Express 托管静态文件
通过 Express 内置的 express.static 可以方便地托管静态文件,例如图片、CSS、JavaScript 文件等。
将静态资源文件所在的目录作为参数传递给 express.static 中间件就可以提供静态资源文件的访问了。例如,假设在 public 目录放置了图片、CSS 和 JavaScript 文件,你就可以:
//直接将public里的index.html当成/的网页
app.use(express.static('public'))
现在,public 目录下面的文件就可以访问了。
http://localhost:3000/images/kitten.jpg
http://localhost:3000/css/style.css
http://localhost:3000/js/app.js
http://localhost:3000/images/bg.png
http://localhost:3000/hello.html
所有文件的路径都是相对于存放目录的,因此,存放静态文件的目录名不会出现在 URL 中。
如果你的静态资源存放在多个目录下面,你可以多次调用 express.static 中间件:
app.use(express.static('public'))
app.use(express.static('files'))
访问静态资源文件时,express.static 中间件会根据目录添加的顺序查找所需的文件。
如果你希望所有通过 express.static 访问的文件都存放在一个“虚拟(virtual)”目录(即目录根本不存在)下面,可以通过为静态资源目录指定一个挂载路径的方式来实现,如下所示:
app.use('/static', express.static('public'))
现在,你就可以通过带有 “/static” 前缀的地址来访问 public 目录下面的文件了。
http://localhost:3000/static/images/kitten.jpg
http://localhost:3000/static/css/style.css
http://localhost:3000/static/js/app.js
http://localhost:3000/static/images/bg.png
http://localhost:3000/static/hello.html
总结
app.use(express.static('public'))
<link rel="stylesheet" href="/css/index.css" />
app.use('/static', express.static('public'))
<link rel="stylesheet" href="/static/css/index.css" />





